数字
偶数减半奇数减一
- 1342. Number of Steps to Reduce a Number to Zero
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class Solution {
public:
int numberOfSteps (int num) {
int count=0,tmp=num;
while(tmp){
if(tmp&1){
tmp--;
}else{
tmp/=2;
}
count++;
}
return count;
}
};
“按位乘积”与”按位和”的差值
- 1281. Subtract the Product and Sum of Digits of an Integer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12class Solution {
public:
int subtractProductAndSum(int n) {
int product=1,sum=0,tmp=n;
while(tmp){
product*=(tmp%10);
sum+=tmp%10;
tmp/=10;
}
return product-sum;
}
};
将k拆分为n个数之和
- 将k拆分为n个数之和,输出所有方案。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
using namespace std;
vector<int> num(10005,0);
int pos=0;
void calK(int k,int last){
if(k==0){
for(int i=0;i<pos;i++){
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}else if(k<0){
return ;
}else{//k>0
for(int i=last;i<=k;i++){
num[pos++]=i;
calK(k-i,i);
pos--;
}
}
}
int main(){
int t;
int k;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>k;
calK(k,1);
}
return 0;
}
数组
3Sum
- 15. 3Sum
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
set<vector<int>> res_tmp;
if(nums.size()<=2) return res;
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
for(int i=0;i<nums.size()-2;++i){
if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1]) continue;
if(nums[i] > 0) break;
int left=i+1, right=nums.size()-1;
while(left<right){
if(nums[left]+nums[right] > (0-nums[i])){
right--;
}else if(nums[left]+nums[right] < (0-nums[i])){
left++;
}else if(nums[left]+nums[right] == (0-nums[i])){
vector<int> tmp;
tmp.push_back(nums[i]);
tmp.push_back(nums[left]);
tmp.push_back(nums[right]);
res_tmp.insert(tmp);
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
for(auto a:res_tmp){
res.push_back(a);
}
return res;
}
};
寻找特殊元素_位运算
136. Single Number
题意:一个元素出现1次,其他元素都出现2次。
思路:
1.可以借助异或的特性,将所有元素异或一遍,剩下的就是出现一次的。
2.扩展一下题目:其他元素都出现偶数次都可以这种方法解决。
3.这种方法的本质是记录二进制上每一位出现的次数,可以看下一题。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18//solution 1
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res=0;
for(auto a:nums){
res^=a;
}
return res;
}
};
//solution 2
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
return accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(),0,bit_xor<int>());
}
};137. Single Number II
题意:数组中有一个元素出现一次,其他都出现3次,找出出现一次的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46//法一:出现一次的位用one记录,2次3次分别用two、three记录。注意先更新two再更新one。
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int one=0,two=0,three=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
two |= one&nums[i];
one ^= nums[i];
three = one&two;
one &= ~three;
two &= ~three;
}
return one;
}
};
//法二:适用于一个元素出现1次,其他出现n次。(n是奇数)
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int bit[32]={0};
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++){
for(auto a:nums){
bit[i] += (a>>i) & 1;
}
res |= (bit[i]%3) << i;
}
return res;
}
};
//法二优化版:优化掉数组
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res=0,count=0;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++){
count=0;
for(auto a:nums){
count += (a>>i) & 1;
}
res |= (count%3) << i;
}
return res;
}
};
//法四:https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4263927.html260. Single Number III
题意:有两个元素a,b出现一次,其他元素都出现2次。
思路:像之前一样异或一遍,只能得到两个出现一次的元素的异或值,这个值肯定不为0,代表a,b肯定有一位是不一样的,所以利用这个不同,将a和b划分到两组元素中,然后用之前的方法异或一遍就得到两个值了。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18class Solution {
public:
vector<int> singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int xorsum=0;
vector<int> res(2,0);
xorsum=accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0,bit_xor<int>());
//xorsum&=(-xorsum);
xorsum&=~(xorsum-1);//这里得到的是a和b二进制位中最右边不同的一位
for(auto a:nums){
if(a&xorsum){
res[0]^=a;
}else{
res[1]^=a;
}
}
return res;
}
};
数组异或
- 1486. XOR Operation in an Array
题意:给start和n,构造start为起点,每个元素间隔2,长度为n的数组,求所有元素异或的结果。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36// https://www.cnblogs.com/hellojamest/p/13179163.html
class Solution {
public:
int xorOperation(int n, int start) {
int result=0;
if((start/2)%2==0){
result=xorA(n,start/2);
}else{
result=(start/2-1) ^ xorA(n+1,start/2-1);
}
result<<=1;
if(n&start&1) result++;
return result;
}
private:
int xorA(int n,int start){
int result=(n/2)&1;
if(n%2==1){
result^=start+n-1;
}
return result;
}
};
/*
class Solution {
public:
int xorOperation(int n, int start) {
int result=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
result^=(start+2*i);
}
return result;
}
};
*/
求每个元素在数组中的排行
- 1365. How Many Numbers Are Smaller Than the Current Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16class Solution {
public:
vector<int> smallerNumbersThanCurrent(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> res;
vector<int> vi(101,0);
for(auto a:nums){
for(int i=a+1;i<=100;i++){
vi[i]++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
res.push_back(vi[nums[i]]);
}
return res;
}
};
解码数组
- 1313. Decompress Run-Length Encoded List
题意:给予[1,2,3,4],代表1个2,3个四,所以返回[2,4,4,4].1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class Solution {
public:
vector<int> decompressRLElist(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> res;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i+=2){
res.insert(res.end(),nums[i],nums[i+1]);
}
return res;
}
};
统计位数为偶数的元素个数
- 1295. Find Numbers with Even Number of Digits
题意:计算数组里位数是偶数的元素有多少个1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16class Solution {
public:
int findNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {
int digitsNumber=0,res=0,tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
digitsNumber=0;
tmp=nums[i];
while(tmp){
tmp/=10;
digitsNumber++;
}
if(!(digitsNumber&1)) res++;
}
return res;
}
};
最大两元素的乘积
- 1464. Maximum Product of Two Elements in an Array
题意:找出最大的两个元素a和b,计算(a-1)*(b-1).1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums) {
int maxx1=max(nums[0],nums[1]),maxx2=min(nums[0],nums[1]);
for(int i=2;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i]>maxx1){
maxx2=maxx1;
maxx1=nums[i];
}else if(nums[i]<=maxx1){
maxx2=max(maxx2,nums[i]);
}
}
return (maxx1-1)*(maxx2-1);
}
};
给定区间问覆盖某点的区间个数
- 1450. Number of Students Doing Homework at a Given Time
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class Solution {
public:
int busyStudent(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, int queryTime) {
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<startTime.size();i++){
if(queryTime>=startTime[i] && queryTime<=endTime[i]) ++res;
}
return res;
}
};
最大连续子序和
- 53. Maximum Subarray
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int maxsum=INT_MIN,maxx=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
maxx=max(maxx,0);
maxx+=nums[i];
maxsum=max(maxsum,maxx);
}
return maxsum;
}
};
重排数组:按要求重排
- 1389. Create Target Array in the Given Order
Input: nums = [0,1,2,3,4], index = [0,1,2,2,1]
Output: [0,4,1,3,2]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class Solution {
public:
vector<int> createTargetArray(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& index) {
vector<int> res;
for(int i=0;i<index.size();i++){
res.insert(res.begin()+index[i],nums[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
重排数组:奇偶交替
-
题意:奇数放到奇数位,偶数放到偶数位,顺序无所谓。给定数组一定是偶数个元素,奇偶数相同。
1 | class Solution { |
重排数组:sort排序
- 179. Largest Number
题意:重排数组,使得重排后”连接数组”组成的数字最大。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13class Solution {
public:
string largestNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int zeronum=0;
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end(),[&](int a,int b){
return (to_string(a)+to_string(b))>(to_string(b)+to_string(a));
});
if(all_of(nums.begin(),nums.end(),[](int i){return i==0;})) return "0";
ostringstream res;
copy(nums.begin(),nums.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(res,""));
return res.str();
}
};
单增数组,前后两段交换后,找最大元素
- 33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
思路:二分法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left=0,right=nums.size()-1;
while(left<right){
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target) return mid;
if(nums[mid]>=nums[left]){
if(target>=nums[left] && target<=nums[mid]){
right=mid-1;
}else{
left=mid+1;
}
}else{
if(target>=nums[mid] && target<=nums[right]){
left=mid+1;
}else{
right=mid-1;
}
}
}
if(nums[left]==target){
return left;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
};
寻找数组中任意一个峰值
- 162. Find Peak Element
题意:数组中寻找任意一个峰值,数组的每个相邻元素都不相等。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46//tc:logn递归版
class Solution {
public:
int findPeakElement(vector<int>& nums) {
return findNum(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
}
private:
int findNum(vector<int> &num,int s,int e){
if((e-s)==0) return e;
if((e-s)==1){
if(num[s]<num[e]){
return e;
}else{
return s;
}
}
int mid=s+(e-s)/2;
if(num[mid-1]<num[mid] && num[mid+1]<num[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(num[mid-1]<num[mid] && num[mid+1]>num[mid]){
return findNum(num,mid+1,e);
}else if(num[mid-1]>num[mid] && num[mid+1]<num[mid]){
return findNum(num,s,mid);
}else{
return findNum(num,s,mid);
}
}
};
//tc:logn迭代二分
//1.采用左闭右开区间。2.区间只有一个值是终止二分。3.mid=(s+e)/2时,左区间是[s,mid),右区间是[mid,e)。
class Solution {
public:
int findPeakElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int s=0,e=nums.size();
while(s+1<e){
int mid=(e+s)/2;
if(nums[mid-1]<nums[mid]){
s=mid;
}else{
e=mid;
}
}
return s;
}
};
无序数组查找中位数
内存够用
- 转为topK问题,借助快速排序思想,当第K大的数归位即退出条件。
内存不够用
- 分桶法,先确定n个数的最小值最大值范围min~max,然后将该范围划分为m份,之后遍历所有数,将每个数字按照符合的范围放到相应文件。(注意要确保每个文件中的数据能在内存放下)
两个有序数组查找中位数
- 4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays
标签:二分、中位数。
思路:题目的关键在于寻找两个数组分别的分割处,可以通过二分较小数组的分割处,来寻找满足条件的分割位置,获取到两个数组的分割位置了,分割位置两边的数就是关键。
参考:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LPFhl65R7ww&t=1013s1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28class Solution {
public:
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int m=nums1.size(),n=nums2.size();
if(m>n) return findMedianSortedArrays(nums2,nums1);
int start=0,end=nums1.size();
while(start<=end){
int partitionX=start+(end-start)/2;
int partitionY=(m+n+1)/2-partitionX;
int xleftmax=(partitionX==0?std::numeric_limits<int>::min():nums1[partitionX-1]);
int xrightmin=(partitionX==m?std::numeric_limits<int>::max():nums1[partitionX]);
int yleftmax=(partitionY==0?std::numeric_limits<int>::min():nums2[partitionY-1]);
int yrightmin=(partitionY==n?std::numeric_limits<int>::max():nums2[partitionY]);
if(xleftmax<=yrightmin && yleftmax<=xrightmin){
if((m+n)%2==0){
return (max(xleftmax,yleftmax)+min(xrightmin,yrightmin))*1.0/2;
}else{
return max(xleftmax,yleftmax);
}
}else if(xleftmax<=yrightmin){
start=partitionX+1;
}else{
end=partitionX-1;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
简单洗牌
- 1470. Shuffle the Array
题意:[x1,x2,…,xn,y1,y2,…,yn] –> [x1,y1,x2,y2,…,xn,yn]。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28// tc:o(n), sc:o(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> shuffle(vector<int>& nums, int n) {
vector<int> result(2*n,0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
result[2*i]=nums[i];
result[2*i+1]=nums[n+i];
}
return result;
}
};
// tc:o(n), sc:o(1)
// 因为每个数最大是1000,先用后半段的数暂时储存前半段,然后从前往后挨个配置
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> shuffle(vector<int>& nums, int n) {
for(int i=n;i<nums.size();i++){
nums[i]=nums[i]*10000+nums[i-n];
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i+=2){
nums[i]=nums[n+i/2]%10000;
nums[i+1]=nums[n+i/2]/10000;
}
return nums;
}
};
前缀和
- 1480. Running Sum of 1d Array
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11class Solution {
public:
vector<int> runningSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> result(nums);
if(nums.size()==0) return result;
for(int i=1;i<result.size();i++){
result[i]+=result[i-1];
}
return result;
}
};
区间和
- 303.Range Sum Query - Immutable
题目描述:没有元素修改的前缀和。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16class NumArray {
public:
//初始化,前缀和
NumArray(vector<int>& nums) {
prefixSum.push_back(0);
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
prefixSum.push_back(prefixSum[i]+nums[i]);
}
}
//求区间和
int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return prefixSum[j+1]-prefixSum[i];
}
private:
vector<int> prefixSum;
};
矩阵
填充螺旋矩阵
- 矩阵样例:
1
2
3
4
5
61 2 3 4 5 6
20 21 22 23 24 7
19 32 33 34 25 8
18 31 36 35 26 9
17 30 29 28 27 10
16 15 14 13 12 11
代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
using namespace std;
int matrix[100][100];
int main()
{
int t;
int countt=1;
cin>>t;
int floor=(t%2==1)?(t+1)/2 : t/2;
for(int i=0;i<floor;i++){
for(int j=i;j<=t-i-1;j++){
matrix[i][j]=countt++;
}
for(int j=i+1;j<=t-i-2;j++){
matrix[j][t-i-1]=countt++;
}
for(int j=t-i-1;j>=i;j--){
matrix[t-i-1][j]=countt++;
}
for(int j=t-i-2;j>=i+1;j--){
matrix[j][i]=countt++;
}
}
if(t%2==1){
matrix[floor-1][floor-1]=t*t;
}
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
for(int j=0;j<t;j++){
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
矩阵每行加一或每列加一
- 1252. Cells with Odd Values in a Matrix
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21class Solution {
public:
int oddCells(int n, int m, vector<vector<int>>& indices) {
int res=0;
vector<vector<int>> matrix(n,vector<int>(m,0));
for(int i=0;i<indices.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
matrix[indices[i][0]][j]++;
}
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
matrix[j][indices[i][1]]++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(matrix[i][j]&1) res++;
}
}
return res;
}
};
水平翻转|按位翻转
- 832. Flipping an Image
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> flipAndInvertImage(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<vector<int>>::iterator vviit=A.begin();
for(vviit;vviit!=A.end();vviit++){
vector<int> tmp;
reverse(vviit->begin(),vviit->end());
for(auto a:*vviit){
if(a==0){
tmp.push_back(1);
}else{
tmp.push_back(0);
}
}
res.push_back(tmp);
}
return res;
}
};
变换01矩阵使得行列都为偶数个1
题意:一个m*n的01矩阵,m、n都是奇数,可以对一行或一列进行取反,问最少操作多少次能让所有行所有列都是偶数个1。
思路:
1.先看对一行进行取反,会导致所有奇数个1的列变为偶数个,所有偶数个1的列变为奇数个。如果对两行取反,奇数个1的列仍然为奇数个,偶数个1的仍然为偶数个。这样就会发现,对奇数个行取反,会导致满足条件和不满足条件列的个数互换;对偶数行取反,不影响满足条件的列的个数。
2.假设不满足条件的行数为r1,满足条件的行数为r2;不满足条件的列数为c1,满足条件的列数为c2.
当r1为偶数,c1为偶数时。对r1行不满足条件的进行取反,对列的数量是不影响的,然后再对c1列取反,res=r1+c1即可完成任务。
当r1为偶数,c1为奇数时,对r1行取反,行全部满足条件了,也不影响列,对奇数c1列取反,又会导致所有行(总共奇数行)不满足条件,这样行列互相影响,无解。
当r1为奇数,c1为偶数时,同上一种。
当r1为奇数,c1为奇数时,分两种情况:(1)先调整r1行,再调整c2列(c2=n-c1),res1=r1+c2;(2)先调整c1列,再调整r2行(r2=m-r1),res2=r2+c1.最少操作为res=min(res1,res2)。
数学
sqrt
- 69. Sqrt(x)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20class Solution {
public:
int mySqrt(int x) {
if(x==1) return 1;
if(x==0) return 0;
long long left=0,right=x;
long long mid=0;
while(true){
mid=left+(right-left)/2;
if(x/mid>=mid && x/(mid+1)<(mid+1)) return mid;
if(x/mid<mid){
right=mid-1;
}else{
left=mid+1;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
素数筛法
-
题意:给定n,输出从1-n之间的素数个数。
1 | class Solution { |
快速幂
递归解法
- 50. Pow(x, n)
思路:针对a^n,如果n是奇数,可以拆分为a (a^(n-1));如果n是偶数,可以拆分为a^(n/2) a^(n/2)。
1 | //版本一,调用两遍pow |
二进制拆分法
思路:以2^11为例,11的二进制是1011,1011=1000+10+1,10进制表示是8+2+1,所以2^11可以拆分为2^8 2^2 2^1。下列代码中,base累积计算2^2、2^4、2^8、…,当n的该位为1,res就乘一下base。
1 | class Solution { |
几何坐标系
- 1266. Minimum Time Visiting All Points
题意:给定若干点的坐标,计算访问所有点的路径之和(可以横、竖、对角线走,每次花费为1).1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class Solution {
public:
int minTimeToVisitAllPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<points.size()-1;i++){
res+=max(abs(points[i][0]-points[i+1][0]),abs(points[i][1]-points[i+1][1]));
}
return res;
}
};
计算逆波兰表达式
- 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
Input: [“2”, “1”, “+”, “3”, ““]
Output: 9
Explanation: ((2 + 1) 3) = 91
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> num;
int n1,n2;
for(int i=0;i<tokens.size();i++){
if(tokens[i][tokens[i].size()-1] >= '0' &&tokens[i][tokens[i].size()-1] <= '9'){
num.push(std::stoi(tokens[i]));
continue;
}
n1=num.top();num.pop();
n2=num.top();num.pop();
if(tokens[i][tokens[i].size()-1]=='+'){
num.push(n2+n1);
}else if(tokens[i][tokens[i].size()-1]=='-'){
num.push(n2-n1);
}else if(tokens[i][tokens[i].size()-1]=='*'){
num.push(n2*n1);
}else if(tokens[i][tokens[i].size()-1]=='/'){
num.push(n2/n1);
}
}
return num.top();
}
};
链表二进制转十进制
- 1290. Convert Binary Number in a Linked List to Integer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34//my second solution
class Solution {
public:
int getDecimalValue(ListNode* head) {
return head ? (res<<=1,res|=head->val,getDecimalValue(head->next)) : res;
}
private:
int res=0;
};
/*
//my first solution
class Solution {
public:
int getDecimalValue(ListNode* head) {
if(head==nullptr) return 0;
return getDecimalValue(head->next)+(head->val ? pow(2,index++) : (index++,0));
}
private:
int index=0;
};
//other people
class Solution {
public:
int getDecimalValue(ListNode* head) {
int ans{};
while (head) {
ans <<= 1;
ans |= head->val;
head = head->next;
}
return ans;
}
};
*/
内部排序
快速排序(5种实现方式)
1 |
|
冒泡排序
1 | class Solution { |
插入排序
选择排序
树型选择排序
归并排序
堆排序
桶排序
希尔排序
外部排序
多路平衡归并排序算法
置换选择排序算法
最佳归并树
链表
链表模拟的大数加法
- 2. Add Two Numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *head=new ListNode(0);
ListNode *iter=head;
ListNode *ptr1=l1, *ptr2=l2;
int digtal=0;
int carry=0;
while(ptr1!=nullptr || ptr2!=nullptr){
digtal=0;
if(ptr1!=nullptr){
digtal+=ptr1->val;
}
if(ptr2!=nullptr){
digtal+=ptr2->val;
}
digtal+=carry;
ListNode *tmp=new ListNode(digtal%10);
carry=digtal/10;
iter->next=tmp;
iter=iter->next;
if(ptr1!=nullptr){
ptr1=ptr1->next;
}
if(ptr2!=nullptr){
ptr2=ptr2->next;
}
}
if(carry!=0){
ListNode *tmp=new ListNode(carry);
iter->next=tmp;
}
iter=head->next;
delete head;
return iter;
}
};
合并两条有序链表
1 | /** |
反转链表的m到n个节点(0<=m<=n<=lenght)
1 | ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { |
判断Y型链表的第一个公共结点
- 我去走你走过的路,你去走我走过的路,然后我们就会相遇。
链表中环的入口
142. Linked List Cycle II
题解:首先设置两个指针,slow每次走一步,fast每次走两步。显而易见,如果存在环,两个指针一定会走到环中,然后快的早晚能追上慢的,就像两人在操场跑步一样。第二步是让两个指针,一个从链表头开始跑,一个从相遇点开始跑,都是每次走一步,两个指针相遇的时候,就是环的入口。第二步的证明如下: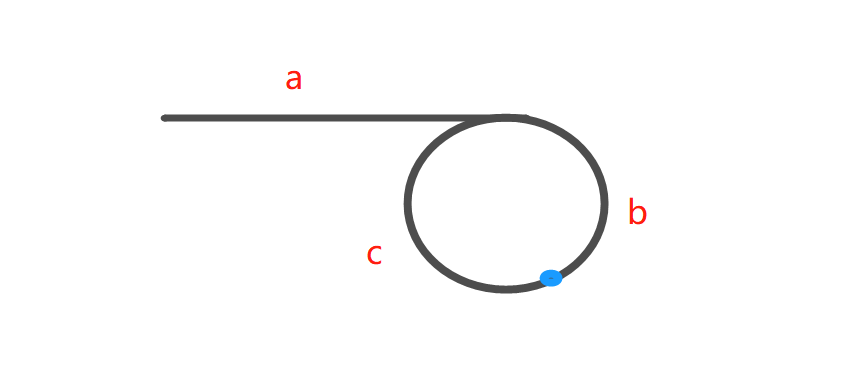
设链表头到环入口的长度为a,从环入口到相遇点长度b,从相遇点到环入口为c。
快指针的路程为:a+(b+c)k+b。(k一定大于等于1,不然快慢指针走的路程岂不是一样了)
慢指针路程:a+b。(慢指针进入环之后,走不完一圈一定会被快指针追上)
快指针路程为慢指针路程的2倍:2(a+b)=a+(b+c)k+b
我们想获取a的值:a=(k-1)(b+c)+c。
所以从链表头到环入口的距离等于从相遇点走到环入口的距离(从相遇点出发的指针可能是第一圈就到达环入口,可能是第2、3…)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr || head->next==nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode *fast=head,*slow=head;
while(fast->next!=nullptr && fast->next->next!=nullptr){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(slow==fast) break;
}
if(fast->next==nullptr || fast->next->next==nullptr) return nullptr;
slow=head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
单链表归并排序
- 148.Sort List
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71/*
1.特殊情况判断
2.将链表二分
3.两条链表分别进行排序
4.归并两条链表
*归并链表两种方式,递归法&顺序合并法
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr) return head;
ListNode *onestep=head,*twostep=head;
while(twostep->next!=nullptr && twostep->next->next!=nullptr){
onestep=onestep->next;
twostep=twostep->next->next;
}
ListNode *secondlist=onestep->next;
onestep->next=nullptr;
return merge2(sortList(head),sortList(secondlist));
}
ListNode *merge(ListNode *first,ListNode *second){
if(first==nullptr) return second;
if(second==nullptr) return first;
if(first->val<second->val){
first->next=merge(first->next,second);
}else{
second->next=merge(first,second->next);
}
return first->val<second->val ? first : second;
}
ListNode *merge2(ListNode *first,ListNode *second){
if(first==nullptr) return second;
if(second==nullptr) return first;
ListNode *firstcurrent=first,*secondcurrent=second,*tmp=nullptr;
if(firstcurrent->val<secondcurrent->val){
tmp=firstcurrent;
firstcurrent=firstcurrent->next;
}else{
tmp=secondcurrent;
secondcurrent=secondcurrent->next;
}
ListNode *newhead=tmp;
while(firstcurrent!=nullptr&&secondcurrent!=nullptr){
if(firstcurrent->val<secondcurrent->val){
tmp->next=firstcurrent;
firstcurrent=firstcurrent->next;
}else{
tmp->next=secondcurrent;
secondcurrent=secondcurrent->next;
}
tmp=tmp->next;
}
if(firstcurrent==nullptr){
tmp->next=secondcurrent;
}else{
tmp->next=firstcurrent;
}
return newhead;
}
};
归并多条链表
- 23. Merge k Sorted Lists
思路:使用优先队列维护每个链表头,每次出队最小的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
struct Node{
int val;
ListNode *ptr;
Node(int v,ListNode *p):val(v),ptr(p){}
bool operator>(const Node &n)const{
return val>n.val;
}
bool operator<(const Node &n)const{
return val<n.val;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
if(lists.size()==0) return nullptr;
initPriorityQueue(lists);//先初始化优先队列
ListNode *head,*p;
head=getMinNode(lists);
if(head==nullptr) return head;
p=head;
ListNode *tmp;
//循环获取最小的链表头
while((tmp=getMinNode(lists)) && tmp!=nullptr){
p->next=tmp;
p=p->next;
p->next=nullptr;
}
return head;
}
private:
//初始化优先队列
void initPriorityQueue(vector<ListNode*> &lists){
for(int i=0;i<lists.size();i++){
if(lists[i]!=nullptr){
q.push(Node(lists[i]->val,lists[i]));
}
}
}
//从优先队列获取最小链表头,并更新优先队列
ListNode* getMinNode(vector<ListNode*> &lists){
if(q.size()!=0){
ListNode *res=q.top().ptr;
q.pop();
if(res->next!=nullptr){
q.push(Node(res->next->val,res->next));
}
return res;
}else{
return nullptr;
}
}
private:
priority_queue<Node,vector<Node>,greater<Node>> q;
};
复制带random指针的链表
字符串
分割平衡串
- 1221. Split a String in Balanced Strings
题意:Input: s = “RLRRLLRLRL”,Output: 4。(RL,RRLL,RL,RL)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class Solution {
public:
int balancedStringSplit(string s) {
int res=0,pos=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
if(s[i]=='R'){
pos++;
}else{
pos--;
}
if(pos==0) res++;
}
return res;
}
};
替换字符串|处理IP地址
- 1108. Defanging an IP Address
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class Solution {
public:
string defangIPaddr(string address) {
string res(address.size()+6,'.');
int index=res.size()-1;
for(int i=address.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
if(address[i]!='.'){
res[index--]=address[i];
}else{
res[index--]=']';
res[index--]='.';
res[index--]='[';
}
}
return res;
}
};
最长不重复子串
- 3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
if(s.size()==0 || s.size()==1) return s.size();
int left=0,right=1;
string longeststr;
longeststr+=s[0];
map<char,int> mapci;
mapci[s[0]]=0;
while(1){
//如果当前map没有该字符,就添加到map,并更新最长字符串
if(mapci.count(s[right])==0){
mapci[s[right]]=right;
if((right-left+1)>longeststr.size()){
longeststr=s.substr(left,right-left+1);
//cout<<longeststr<<endl;
}
}else{
如果出现重复字符,首先判断当前串是否更长
if((right-left)>longeststr.size()){
longeststr=s.substr(left,right-left+1);
//cout<<longeststr<<endl;
}
//从map中删除从left到重复字符的位置
int t=mapci[s[right]]+1;
for(int i=left;i<=mapci[s[right]];i++){
mapci.erase(s[i]);
}
更新left并将right字符位置添加到map
left=t;
mapci[s[right]]=right;
}
right++;
if(right==s.size()){
break;
}
}
return longeststr.size();
}
};
/*
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int n=s.size(),ans=0,i=0;
vector<int> lastIndex(256,-1);
for(int j=0;j<n;++j) {
i=max(i,lastIndex[s[j]]+1);
ans=max(ans,j-i+1);
lastIndex[s[j]]=j;
}
return ans;
}
*/
kmp模式匹配
1 |
字符串逆置
1 | void reversestr(string &str){ |
其他
- 771.Jewels and Stones
题意:给定字符串J和S,判断S中有多少字符在J中出现,J中无重复字符,且大小写敏感。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15// tc:o(n+m)
class Solution {
public:
int numJewelsInStones(string J, string S) {
int res=0;
unordered_map<char,int> m;
for(auto a:J){
m[a]++;
}
for(auto a:S){
if(m[a]!=0) res++;
}
return res;
}
};
动态规划
01背包
1 | int a[1005]={0};//全局数组 |
完全背包
1 | int a[1005]={0}; |
多重背包
1 | int a[1005]; |
分割字符串
- 139. Word Break
题目描述:给定字符串s,判断能否分割为字典wordDict中的单词(wordDict中无重复单词,但s分割开的可以重复).1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57//法一:动态规划
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
int n=s.size(),m=wordDict.size();
vector<bool> dp(n+2,false);
dp[0]=true;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int index=i;
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(s.substr(index,wordDict[j].size())==wordDict[j] && dp[index]==true){
dp[index+wordDict[j].size()]=true;
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
/*
//暴力遍历+set优化
class Solution {
public:
bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) {
if(s.size()==0) return true;
set<string> dict; //优化去字典查找的速度。
set<int> num; //优化状态。
for(auto s:wordDict){
dict.insert(s);
}
queue<int> queuestr;
queuestr.push(0);
while(!queuestr.empty()){
int index=queuestr.front(); queuestr.pop();
string tmp="";
for(int i=index;i<s.size();i++){
tmp+=s[i];
if(i==s.size()-1){
if(dict.count(tmp)!=0){
return true;
}else{
break;
}
}
if(dict.count(tmp)!=0){
if(num.count(i+1)==0){
queuestr.push(i+1);
num.insert(i+1);
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
auto sync=[](){ios::sync_with_stdio(false);};
*/
树
二叉树
先序遍历(三种方法)
- 144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
/* Morris先序遍历
先序遍历中,访问顺序是根左右,其中根左是很容易的,重点在于根左完了之后需要访问根的右子树。
无论是递归版还是用栈模拟的版本,都保存了根节点的索引,这样可以方便的找到右子树。
在morris方式中,巧妙地利用了叶子节点里的空闲指针。
假如当前根节点为cur,此时如果马上下到左子树上,就会丢失cur节点。
所以可以找到cur左子树的最右下的那个叶子结点,将它的右指针指向cur。
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
TreeNode *cur=root,*tmp;
while(cur!=nullptr){
if(cur->left==nullptr){
res.insert(res.end(),cur->val);
cur=cur->right;
}else{
tmp=cur->left;
while(tmp->right!=nullptr && tmp->right!=cur){
tmp=tmp->right;
}
if(tmp->right==nullptr){
res.insert(res.end(),cur->val);
tmp->right=cur;
cur=cur->left;
}else{
tmp->right=nullptr;
cur=cur->right;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
/*
//递归版
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> res;
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
return preorderRecursive(root),res;
}
void preorderRecursive(TreeNode *root){
if(root==nullptr) return;
res.insert(res.end(),root->val);
preorderRecursive(root->left);
preorderRecursive(root->right);
}
};
//stack 迭代版
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode *> sta;
sta.push(root);
TreeNode *tmp;
while(!sta.empty()){
tmp=sta.top(); sta.pop();
res.push_back(tmp->val);
if(tmp->right!=nullptr) sta.push(tmp->right);
if(tmp->left!=nullptr) sta.push(tmp->left);
}
return res;
}
};
*/
中序遍历(三种方法)
- 94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//Morris版时间复杂度O(n),空间O(1).但实测不如另外两种快?
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
TreeNode *cur=root,*tmp;
while(cur!=nullptr){
if(cur->left==nullptr){
res.insert(res.end(),cur->val);
cur=cur->right;
}else{
tmp=cur->left;
while(tmp->right!=nullptr && tmp->right!=cur){
tmp=tmp->right;
}
if(tmp->right==cur){
tmp->right=nullptr;
res.insert(res.end(),cur->val);
cur=cur->right;
}else{
tmp->right=cur;
cur=cur->left;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
/*
//递归
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> res;
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
return inorderRecursive(root),res;
}
void inorderRecursive(TreeNode *root){
if(root==nullptr) return;
inorderRecursive(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
inorderRecursive(root->right);
}
};
//stack 迭代
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode *> sta;
TreeNode *tmp=root;
while(tmp!=nullptr || !sta.empty()){
while(tmp!=nullptr){
sta.push(tmp);
tmp=tmp->left;
}
tmp=sta.top(); sta.pop();
res.push_back(tmp->val);
tmp=tmp->right;
}
return res;
}
};
*/
后序遍历(三种方法)
- 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//Morris版
//使用revertmp的版本,空间复杂度不是o(1),最坏情况是o(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
TreeNode newroot(0); newroot.left=root;
TreeNode *cur=&newroot,*tmp;
while(cur!=nullptr){
if(cur->left==nullptr){
cur=cur->right;
}else{
tmp=cur->left;
while(tmp->right!=nullptr && tmp->right!=cur){
tmp=tmp->right;
}
if(tmp->right==nullptr){
tmp->right=cur;
cur=cur->left;
}else{
vector<int> revertmp;//最坏o(n)
tmp->right=nullptr;
tmp=cur->left;
while(tmp!=nullptr){
revertmp.insert(revertmp.begin(),tmp->val);
tmp=tmp->right;
}
res.insert(res.end(),revertmp.begin(),revertmp.end());
cur=cur->right;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
/*
//递归版
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> res;
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
postorderRecursive(root);
return res;
}
void postorderRecursive(TreeNode *root){
if(root==nullptr) return ;
postorderRecursive(root->left);
postorderRecursive(root->right);
res.insert(res.end(),root->val);
}
};
//栈 迭代版
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> snode;
vector<int> vires;
if(root!=NULL){
snode.push(root);
}
while(!snode.empty()){
TreeNode* now=snode.top(); snode.pop();
vires.push_back(now->val);
if(now->left!=NULL){
snode.push(now->left);
}
if(now->right!=NULL){
snode.push(now->right);
}
}
reverse(vires.begin(),vires.end());
return vires;
}
};
*/
层次遍历(分层返回)
- 102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<pair<TreeNode *,int>> que;
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root==nullptr) return res;
vector<int> tmp;
tmp.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left==nullptr && root->right==nullptr) return res.push_back(tmp),res;
if(root->left!=nullptr) que.push({root->left,2});
if(root->right!=nullptr) que.push({root->right,2});
int lastfloor=1;
while(!que.empty()){
pair<TreeNode *,int> now=que.front(); que.pop();
if(now.second!=lastfloor){//如果是新的一层,则将tmp加到res中
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.erase(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
tmp.push_back(now.first->val);
if(now.first->left!=nullptr) que.push({now.first->left,now.second+1});
if(now.first->right!=nullptr) que.push({now.first->right,now.second+1});
lastfloor=now.second;
}else{//同一层都加到tmp中
tmp.push_back(now.first->val);
if(now.first->left!=nullptr) que.push({now.first->left,now.second+1});
if(now.first->right!=nullptr) que.push({now.first->right,now.second+1});
lastfloor=now.second;
}
}
res.push_back(tmp);
return res;
}
};
/*递归版
vector<vector<int>> ret;
void buildVector(TreeNode *root, int depth)
{
if(root == NULL) return;
if(ret.size() == depth)
ret.push_back(vector<int>());
ret[depth].push_back(root->val);
buildVector(root->left, depth + 1);
buildVector(root->right, depth + 1);
}
vector<vector<int> > levelOrder(TreeNode *root) {
buildVector(root, 0);
return ret;
}
*/
遍历相关变型
- 938. Range Sum of BST
题意:统计二叉搜索树中L~R之间的数之和。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14//可以利用二叉搜索树特性再剪枝优化
class Solution {
public:
int rangeSumBST(TreeNode* root, int L, int R) {
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
int tmp=0;
tmp+=rangeSumBST(root->left,L,R);
if(root->val>=L && root->val<=R){
tmp+=root->val;
}
tmp+=rangeSumBST(root->right,L,R);
return tmp;
}
};
图
有向图
- 207.Course Schedule
题目描述:判断有向图中是否存在环/拓扑排序。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39/*
1.BFS法:每次挑选图中入度为0的点,去除与其相连的边。
邻接矩阵graph表示有向图,
inNumber表示每个点的入度数量,
inNumberIsZero为队列,存储入度为0的点
1 初始化邻接矩阵、入度数量矩阵
2 将入度为0的点入队
3 每次从队列中取出入度为0的点,然后去除该点出发的所有边
去除边后,发现有入度为0的点,就继续入队。
4 判断是否有点入度不为0.
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
vector<int> inNumber(numCourses,0);
queue<int> inNumberIsZero;
for(auto a:prerequisites){
graph[a[1]].push_back(a[0]);
inNumber[a[0]]++;
}
for(int i=0;i<inNumber.size();i++){
if(inNumber[i]==0) inNumberIsZero.push(i);
}
while(!inNumberIsZero.empty()){
int tmp=inNumberIsZero.front(); inNumberIsZero.pop();
for(int i=0;i<graph[tmp].size();i++){
inNumber[graph[tmp][i]]--;
if(inNumber[graph[tmp][i]]==0){
inNumberIsZero.push(graph[tmp][i]);
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<inNumber.size();i++){
if(inNumber[i]!=0) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
1 | /* |
无向图
复杂数据结构
树状数组
xxx
红黑树
线段树
单点修改,区间查询的区间和问题
- 307.Range Sum Query - Mutable
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90//线段树是利用二分思想解决区间问题
class SegmentTreeNode{
public:
SegmentTreeNode(int start,int end,int sum,
SegmentTreeNode *left=nullptr,SegmentTreeNode *right=nullptr):
start(start),end(end),sum(sum),left(left),right(right) {}
//禁用赋值构造和拷贝构造函数
SegmentTreeNode(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
SegmentTreeNode& operator=(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
~SegmentTreeNode(){
delete left;
delete right;
left=right=nullptr;
}
public:
int start;
int end;
int sum; //可以是max,min
SegmentTreeNode *left;
SegmentTreeNode *right;
}; //end class SegmentTreeNode
class NumArray {
public:
NumArray(vector<int>& nums) {
nums_.swap(nums);
if(!nums_.empty()){
root_.reset(buildTree(0,nums_.size()-1));
}
}
void update(int i, int val) {
updateTree(root_.get(),i,val-nums_[i]);
}
int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return sumRange(root_.get(),i,j);
}
private:
//创建线段树
SegmentTreeNode *buildTree(int start,int end){
if(start==end){
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,nums_[start]);
}
int mid=start+((end-start)>>1);
SegmentTreeNode *left=buildTree(start,mid);
SegmentTreeNode *right=buildTree(mid+1,end);
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,left->sum+right->sum,left,right);
}
//更新线段树,将i处的值增加addval
void updateTree(SegmentTreeNode *root,int i,int addval){
if(root->start==i && root->end==i){
root->sum+=addval;
nums_[i]+=addval;
return ;
}
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(i<=mid){
updateTree(root->left,i,addval);
}else{
updateTree(root->right,i,addval);
}
root->sum+=addval;
}
//计算区间i到j的和
int sumRange(SegmentTreeNode *root,int i,int j){
if(root->start==i && root->end==j){
return root->sum;
}
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(i>mid){
return sumRange(root->right,i,j);
}else if(j<=mid){
return sumRange(root->left,i,j);
}else{
return sumRange(root->left,i,mid)+sumRange(root->right,mid+1,j);
}
}
/* 打印叶子节点,用于调试
void printTree(SegmentTreeNode *root){
if(root->left==nullptr && root->right==nullptr){
cout<<root->sum<<" ";
return ;
}
printTree(root->left);
printTree(root->right);
}
*/
private:
vector<int> nums_;
std::unique_ptr<SegmentTreeNode> root_;
}; //end class NumArray
区间修改,单点查询
- hdu 1556 Color the ball
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
using namespace std;
class SegmentTreeNode{
public:
SegmentTreeNode(int start,int end,int sum,int val=0,SegmentTreeNode *left=nullptr,SegmentTreeNode *right=nullptr):
start(start),end(end),sum(sum),updateval(val),left(left),right(right) {}
//禁用赋值构造和拷贝构造函数
SegmentTreeNode(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
SegmentTreeNode& operator=(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
~SegmentTreeNode(){
delete left;
delete right;
left=right=nullptr;
}
public:
int start;
int end;
int sum; //可以是max,min
int updateval; //用来记录当前区间上update过的数值
SegmentTreeNode *left;
SegmentTreeNode *right;
}; //end class SegmentTreeNode
class NumArray {
public:
NumArray(vector<int>& nums) {
nums_.swap(nums);
if(!nums_.empty()){
root_.reset(buildTree(0,nums_.size()-1));
}
}
void update(int s, int e, int val) {
updateTree(root_.get(),s,e,val);
}
int query(int i) {
return queryTree(root_.get(),i);
}
private:
//创建线段树
SegmentTreeNode *buildTree(int start,int end){
if(start==end){
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,nums_[start]);
}
int mid=start+((end-start)>>1);
SegmentTreeNode *left=buildTree(start,mid);
SegmentTreeNode *right=buildTree(mid+1,end);
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,left->sum+right->sum,0,left,right);
}
//区间更新线段树,将区间s~e处的值增加addval
void updateTree(SegmentTreeNode *root,int s,int e,int val){
if(root->start==s && root->end==e){
root->updateval+=val;
return ;
}
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(s>mid){
updateTree(root->right,s,e,val);
}else if(e<=mid){
updateTree(root->left,s,e,val);
}else{
updateTree(root->left,s,mid,val);
updateTree(root->right,mid+1,e,val);
}
}
//单点查询
int queryTree(SegmentTreeNode *root,int i){
if(root->start==i && root->end==i){
return root->sum+root->updateval;
}
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(i<=mid){
return queryTree(root->left,i)+root->updateval;
}else{
return queryTree(root->right,i)+root->updateval;
}
}
private:
vector<int> nums_;
std::unique_ptr<SegmentTreeNode> root_;
}; //end class NumArray
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int N;
int a,b;
while(cin>>N){
if(N==0) break;
vector<int> tmp(N+1,0);
NumArray numarry(tmp);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
cin>>a>>b;
numarry.update(a,b,1);
}
if(N==1){
cout<<numarry.query(1);
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
cout<<numarry.query(i+1);
if(i!=N-1){
cout<<" ";
}else{
cout<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
区间修改,区间查询
- 洛谷oj:P3372【模板】线段树1
以下有两个版本,第一个是pushdown版本。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
using namespace std;
class SegmentTreeNode{
public:
SegmentTreeNode(int start,int end,long long sum,long long val=0,SegmentTreeNode *left=nullptr,SegmentTreeNode *right=nullptr):
start(start),end(end),sum(sum),updateval(val),left(left),right(right) {}
//禁用赋值构造和拷贝构造函数
SegmentTreeNode(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
SegmentTreeNode& operator=(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
~SegmentTreeNode(){
delete left;
delete right;
left=right=nullptr;
}
public:
int start;
int end;
long long sum; //可以是max,min
long long updateval; //用来记录当前区间上update过的数值
SegmentTreeNode *left;
SegmentTreeNode *right;
}; //end class SegmentTreeNode
class NumArray {
public:
NumArray(vector<long long>& nums) {
nums_.swap(nums);
if(!nums_.empty()){
root_.reset(buildTree(0,nums_.size()-1));
}
}
void update(int s, int e, int val) {
updateTree(root_.get(),s,e,val);
}
long long query(int s,int e) {
return queryTree(root_.get(),s,e);
}
private:
//创建线段树
SegmentTreeNode *buildTree(int start,int end){
if(start==end){
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,nums_[start]);
}
int mid=start+((end-start)>>1);
SegmentTreeNode *left=buildTree(start,mid);
SegmentTreeNode *right=buildTree(mid+1,end);
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,left->sum+right->sum,0,left,right);
}
//区间更新线段树,将区间s~e处的值增加addval
void updateTree(SegmentTreeNode *root,int s,int e,int val){
if(root->start==s && root->end==e){
root->sum+=val*(e-s+1);
root->updateval+=val;
return ;
}
pushdown(root);
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(s>mid){
updateTree(root->right,s,e,val);
}else if(e<=mid){
updateTree(root->left,s,e,val);
}else{
updateTree(root->left,s,mid,val);
updateTree(root->right,mid+1,e,val);
}
root->sum=root->left->sum+root->right->sum;
}
//区间查询
long long queryTree(SegmentTreeNode *root,int s,int e){
if(root->start==s && root->end==e){
return root->sum;
}
pushdown(root);
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(e<=mid){
return queryTree(root->left,s,e);
}else if(s>mid){
return queryTree(root->right,s,e);
}else{
return queryTree(root->left,s,mid)+queryTree(root->right,mid+1,e);
}
}
void pushdown(SegmentTreeNode *root){
if(root->updateval){
root->left->updateval+=root->updateval;
root->right->updateval+=root->updateval;
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
root->left->sum+=root->updateval*(mid-root->start+1);
root->right->sum+=root->updateval*(root->end-mid);
root->updateval=0;
}
}
private:
vector<long long> nums_;
std::unique_ptr<SegmentTreeNode> root_;
}; //end class NumArray
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
long long n,m;
long long tmp,oper,x,y,k;
vector<long long> vi;
cin>>n>>m;
vi.resize(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>vi[i];
}
NumArray numarry(vi);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
cin>>oper;
if(oper==1){
cin>>x>>y>>k;
numarry.update(x,y,k);
}else{
cin>>x>>y;
cout<<numarry.query(x,y)<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}标记永久化版本,去掉了pushdown函数,比上一版本有一常数优化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
using namespace std;
class SegmentTreeNode{
public:
SegmentTreeNode(int start,int end,long long sum,long long val=0,SegmentTreeNode *left=nullptr,SegmentTreeNode *right=nullptr):
start(start),end(end),sum(sum),updateval(val),left(left),right(right) {}
//禁用赋值构造和拷贝构造函数
SegmentTreeNode(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
SegmentTreeNode& operator=(const SegmentTreeNode&)=delete;
~SegmentTreeNode(){
delete left;
delete right;
left=right=nullptr;
}
public:
int start;
int end;
long long sum; //可以是max,min
long long updateval; //用来记录当前区间上update过的数值
SegmentTreeNode *left;
SegmentTreeNode *right;
}; //end class SegmentTreeNode
class NumArray {
public:
NumArray(vector<long long>& nums) {
nums_.swap(nums);
if(!nums_.empty()){
root_.reset(buildTree(0,nums_.size()-1));
}
}
void update(int s, int e, int val) {
updateTree(root_.get(),s,e,val);
}
long long query(int s,int e) {
return queryTree(root_.get(),s,e);
}
private:
//创建线段树
SegmentTreeNode *buildTree(int start,int end){
if(start==end){
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,nums_[start]);
}
int mid=start+((end-start)>>1);
SegmentTreeNode *left=buildTree(start,mid);
SegmentTreeNode *right=buildTree(mid+1,end);
return new SegmentTreeNode(start,end,left->sum+right->sum,0,left,right);
}
//区间更新线段树,将区间s~e处的值增加addval
void updateTree(SegmentTreeNode *root,int s,int e,int val){
root->sum+=val*(e-s+1); //每次调用该函数,只有整棵线段树的根节点到目标结点的sum值会被更新
if(root->start==s && root->end==e){
root->updateval+=val;
return ;
}
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(s>mid){
updateTree(root->right,s,e,val);
}else if(e<=mid){
updateTree(root->left,s,e,val);
}else{
updateTree(root->left,s,mid,val);
updateTree(root->right,mid+1,e,val);
}
}
//区间查询
long long queryTree(SegmentTreeNode *root,int s,int e){
if(root->start==s && root->end==e){
return root->sum;
}
int mid=root->start+((root->end-root->start)>>1);
if(e<=mid){
return queryTree(root->left,s,e)+root->updateval*(e-s+1);
}else if(s>mid){
return queryTree(root->right,s,e)+root->updateval*(e-s+1);
}else{
return queryTree(root->left,s,mid)+queryTree(root->right,mid+1,e)+root->updateval*(e-s+1);
}
}
private:
vector<long long> nums_;
std::unique_ptr<SegmentTreeNode> root_;
}; //end class NumArray
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
long long n,m;
long long tmp,oper,x,y,k;
vector<long long> vi;
cin>>n>>m;
vi.resize(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>vi[i];
}
NumArray numarry(vi);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
cin>>oper;
if(oper==1){
cin>>x>>y>>k;
numarry.update(x,y,k);
}else{
cin>>x>>y;
cout<<numarry.query(x,y)<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
排列组合
全错排问题
题意:有写给不同人的10封信,分别装到不同地址的10个信封中,要求不能有任意一个人收到正确地信,问多少种方案。
思路:1.首先再明确一下全错排问题的定义,重排n个元素,要求每个元素新位置都不是原来的位置。
2.假设当前n封信分别正确装到n个信封中了,我们先将n号信错排,它有n-1种可能。假设n号信占用的是k号信封,此时我们要给k号信找位置,此时有分两种情况。
如果将k号信放到了n号信封,那么就相当于n号信和k号信交换了位置(解决第n封信的全错排问题有n-1种方案),然后剩下的n-2封信也是面临全错排问题即F(n-2)种可能。
如果将k号不放到n号信封(可以看做n号信封是k号信的正确位置),除了k号信和n号信的其他n-2封信也都不能放到原位置。这样n-2加第k号信总共n-1封信,又构成一个全错排问题,即F(n-1).
所以递推公式F(n)=(n-1)*(F(n-1)+F(n-2));
- hdu 1465 不容易系列之一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long n;
vector<long long> f(1005,0);
f[2]=1;
for(long long i=3;i<=1000;i++){
f[i]=(i-1)*(f[i-1]+f[i-2]);
}
while(cin>>n){
cout<<f[n]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
其他面试题
大数组排序
外部排序
对小文件归并排序
topK问题
- n很小,k很小,快速选择算法。
- n很大,k很小,大顶堆。
- n很大,k很大,外部排序,取前k个数。
页面置换算法
LRU(最近最久未使用)
- LeetCode 146. LRU Cache
题意:get操作,如果key在缓存,返回其val并更新访问。未在缓存返回-1。
put操作,key在缓存对其更新(更新val和访问次序)。不在缓存则插入,如果超出容量,删除最久未访问的那个key。
思路:需要维护访问次序,选择list。需要快速判断是否在缓存,选择unordered_map,更新操作可以分为删除原key,插入新key,所以unordered_map的val应当记录key在list中的位置。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41static int __=[](){std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);return 0;}();
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
pageNumber=capacity;
}
//如果访问页在内存中,返回其value并更新该key。如果访问页不在,返回-1。
int get(int key) {
auto it=pageToCache.find(key);
if(it==pageToCache.end()){
return -1;
}
pair<int,int> tmp=*(it->second);
cache.erase(it->second);
cache.push_front(tmp);
pageToCache[key]=cache.begin();
return tmp.second;
}
//如果要设置的页不在内存,则插入该页,并判断是否超出限制。如果该页在内存,则更新该页。
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it=pageToCache.find(key);
pair<int,int> tmp(key,value);
if(it!=pageToCache.end()){
(*(it->second)).second=value;
cache.erase(it->second);
cache.push_front(tmp);
pageToCache[key]=cache.begin();
}else{
cache.push_front(tmp);
pageToCache[key]=cache.begin();
if(cache.size()>pageNumber){
pageToCache.erase(cache.back().first);
cache.pop_back();
}
}
}
private:
list<pair<int,int>> cache;
unordered_map<int,list<pair<int,int>>::iterator> pageToCache;
int pageNumber;
};
LFU(最少使用算法)
- 460 LFU Cache
题意:LFU是最少使用算法,所以在需要将页面置换出去时,就选择一个访问频率最小的。
我们需要提供get()和put()两个操作。对于get(key),如果该key不在缓存,就返回-1,。如果在缓存内,就返回其value并且将其频率更新。对于put(key,val),如果该key在缓存中,就将其val更新,频率更新。如果不在缓存,就看缓存是否已满,如果缓存满了,就选择一个访问频率最低的删除。然后再插入新的(key,val,频率1)。(注意一旦页面被置换出去,频率清零。另外get和put都会增加访问频率)
思路:根据题意,我们需要一个快速判断当前key是否在缓存的一个操作,要求时间复杂度o(1),可以选用unordered_map。另外需要存着key-val并且能够快速寻找访问频率最小的key,于是可以将不同的key-val按照访问频率给分类,应该可以用vector<list>或者unordered_map<int,list >吧,下面是选用的后者。(还要注意当有多个访问频率相同的key-val时,要选择最久未访问的。所以每次删除key-val时,删除的是链表尾,更新key-val时,将其插入到链表头。) 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65struct Node{
int key;
int val;
int freq;
Node(int k,int v,int f):key(k),val(v),freq(f){}
};
class LFUCache {
public:
LFUCache(int _capacity):minfreq(0),capacity(_capacity) {}
int get(int key) {
if(capacity==0) return -1;
auto it=cache.find(key);
//未找到该key,返回-1;
if(it==cache.end()) return -1;
int val=it->second->val,freq=it->second->freq;
//从访问频率freq的链表中删除key
freq_page[freq].erase(it->second);
if(minfreq==freq && freq_page[freq].size()==0) minfreq++;
//将访问的key更新其freq,并存到freq+1处的链表上。
freq_page[freq+1].push_front(Node(key,val,freq+1));
//更新hash表中的指针
cache[key]=freq_page[freq+1].begin();
return val;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
//如果容量为0,则退出
if(capacity==0) return ;
auto it=cache.find(key);
//如果hash表中没有该key,需要添加当前key value
if(it==cache.end()){
//如果当前容量满了,需要先删除访问频率最小的那页,再添加新页
if(cache.size()==capacity){
int lastkey=freq_page[minfreq].back().key;
freq_page[minfreq].pop_back();
if(freq_page[minfreq].size()==0) minfreq++;
cache.erase(lastkey);
}
//添加新的一页
freq_page[1].push_front(Node(key,value,1));
minfreq=1;
cache[key]=freq_page[1].begin();
}else{ //如果hash表中有该key,则更新其value,跟get()操作相似
int freq=it->second->freq;
freq_page[freq].erase(it->second);
if(minfreq==freq && freq_page[minfreq].size()==0) minfreq++;
freq_page[freq+1].push_front(Node(key,value,freq+1));
cache[key]=freq_page[freq+1].begin();
}
}
private:
int minfreq;//最小频率
int capacity;//缓存容量
unordered_map<int,list<Node>::iterator> cache; //key:key,value:key在freq_page中对应链表里的结点位置。
unordered_map<int,list<Node>> freq_page; //key是访问频率,value是处于该访问频率的那些结点。
};
/**
* Your LFUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LFUCache* obj = new LFUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
给定0返回1&给定1返回0
题意:给定一个有符号整数,如果是0则返回1,如果是1则返回0,多种方法求解。
1 | int judge1(int a){ |
计算输入的位数
- sprintf或fprintf返回值是字符个数。
- 十进制数字的或借助log。
- 除以10再右移。
常见的树结构
二叉树
- 一棵树,每个节点可以有0-2个子节点。
满二叉树
- 每个节点都有两个子节点。
- 第k层的结点数为2^(k-1)
- 总结点数为2^k-1
完全二叉树
- 将树从上到下从左到右编号正好是1-n,中间没有空节点。或者说除了最下面一层,上面是个满二叉树,最下面一层的结点都在左边。
- n0是度为0的结点,即叶子节点。N为总结点。两者关系为:2 n0 - 1 = N(N为奇数) 或 2 n0 = N(N为偶数)
1 | 设完全二叉树中度为i的节点为ni,总节点数为N,总树枝数为b,则有: |
二叉搜索树
- 对于每个结点来说,左子树的值都小于当前结点,右子树的值都大于当前结点。
- 插入一个完全有序的序列会导致树退化成链表。
平衡二叉树/AVL树
- 平衡二叉树一定是一棵二叉搜索树,只不过多了“平衡”的特点。
- 平衡二叉树始终保证每个结点的左右子树高度查小于等于1.
b树/b-树
1.定义&性质
- b树是一个m叉的平衡树。
- 一个m(m>2)阶的B树有以下性质:
1
2
3
4
5每一个节点最多有 m 个子节点
每一个非叶子节点(除根节点)最少有 ⌈m/2⌉ 个子节点
如果根节点不是叶子节点,那么它至少有两个子节点
有 k 个子节点的非叶子节点拥有 k − 1 个键(该结点有k个指针,k-1个元素)
所有的叶子节点都在同一层
2.特性
- 每个结点都储存数据。
- 读写的时间复杂度最好o(1),最坏o(logn),所以时间上是不稳定的。
- 每个结点都存储数据,做范围查询时效率不高。
3.应用
- 文件系统
- MongoDB的索引
b+树
1.定义&性质
- b+树也是一个m叉的平衡树,但是与b树有几处不同:(1)非叶子结点上不储存数据,所有数据都储存在叶子节点上。(2)每个结点上子结点指针数量和键数量相同。(3)所有叶子结点都在一层,并且从左到右是用一个链表串起来的。
- 一个m阶b+树有以下性质:
1
2
3
4
5每个结点至多有m个子结点。
除根结点外,每个结点至少有ceil(m/2)个子结点
根结点至少有两个子结点。
一个结点有k个子结点,就有k个关键字。
所有叶子结点在同一层
2.特点
- 只有叶子节点存储数据。非叶子结点不存储数据,只作索引用。
- 每次操作,时间复杂度都是logn
- 方便作范围查询。
3.应用
- 数据库索引
红黑树
线段树
字典树
哈弗曼树
败者树
胜者树
主席树
莫尔斯编码|去重
- 804. Unique Morse Code Words
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class Solution {
public:
int uniqueMorseRepresentations(vector<string>& words) {
map<string,int> m1;
string morse[30]={".-","-...","-.-.","-..",".","..-.","--.","....","..",".---","-.-",".-..","--","-.","---",".--.","--.-",".-.","...","-","..-","...-",".--","-..-","-.--","--.."};
for(auto a : words){
string tmp="";
for(auto a2: a){
tmp+=morse[a2-'a'];
}
m1[tmp]++;
}
return m1.size();
}
};
场景题
- 2G内存100G日志(日志中全是uid),计算出现频率前10的uid。
思路:分100块读取日志,即每次读取1G,用map找出频率前10的uid。这样总共有10*100=1000个uid,然后转化为排序或topK问题。